How to Startup Inside Sales in Just 3 Steps

Table of Contents
What is inside sales?
Inside sales is a role that focuses on finding quality leads with prospecting calls and emails, as opposed to in-person communication. People tend to confuse them with telemarketers, sales reps who only sell through the phone, but they are completely different jobs. Inside sales are also thought to be the team that just responds to inquiries, but that is not their main job.
Why does inside sales matter?
For one, if you can specify the exact role of each sales rep, they can focus on just one task, rather than juggling tons of responsibilities. This way, they can quickly gain skill in their role and start getting better results than if they were stretched to accomplish a bunch of different tasks, like finding viable leads, sales calls, sales meetings, handling contracts, and so on.
Also, studies have found that people are more efficient and work faster when they only have a single task to accomplish, rather than when they have to multitask, and therefore you can reduce the work hours of your whole sales team.
Lastly, by integrating IS, you can spread the responsibility out throughout the team, and nurture multiple skilled sales reps, and avoid becoming dependent on a single expert salesman. This is very important because a company’s sales revenue can crumble when their star sales rep quits and leaves them.
For the above reasons, creating an inside sales role within your team can lead to more productivity and better results.
What is the role of inside sales?
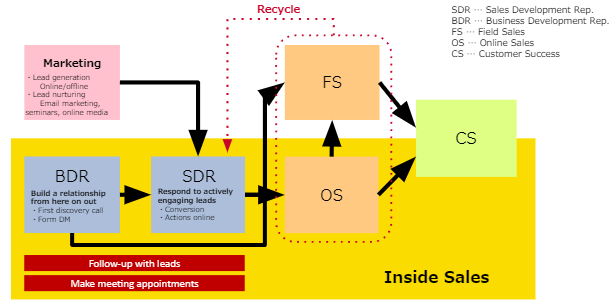
The image above illustrates a typical sales organization, made up of marketing, inside sales (SDR and BDR), account executives (FS and OS), and customer success (CS).
Firstly, the inside sales team is made up of two distinct roles: the business development reps (BDRs), and sales development reps (SDRs). BDRs focus on finding new prospects through outbound methods, and then build the relationship from zero. SDRs take an inbound approach and instead reach out to leads that are engaging with your site or content online, or those who made an inquiry or had a conversion, and give them a call to check into their current needs. The SDR determines if they are a hot lead or not, and then passes them onto the account executives.
Account executives also come in two types, known as field sales (FS) and online sales (OS). Both field sales and online sales are responsible for taking meetings and closing sales. The difference is just that field sales make physical visits to the customer to meet in person, whereas online sales hold all the meetings virtually, like over Zoom or Microsoft Teams. In 2022, many companies only have online sales teams at this point, since field sales became largely obsolete during the pandemic.
Lastly, once the contract is reached, and the customer begins using the service, generally a customer success (CS) team will handle them from that point on. Customer success works to guide them through onboarding, and shows the client how to best use the product to reach their goals.
Important inside sales KPIs
- Number of activities completed
- Call-to-connect ratio / Response rate
- Number of meetings scheduled
- Number of sales closed from qualified prospects
- Average deal size
- Length of sales cycle
- Number of leads gathered by BDRs
How to set up inside sales in 3 steps
1. Prepare content to measure the interest level of leads
The first step is to create content that can be used as a basis for determining the interest level of your leads. On your websites, you’ll need a variety of pages that people of different interest levels are likely to click on - like someone who’s just starting to consider might click on your blog, case studies, and your product overviews, whereas someone with more solidified needs might click on the pricing page or the inquiry page.
Next you should prepare email newsletters and campaigns for both your entire list, but also for smaller segments and hot leads specifically. Then by either using a marketing automation tool or a basic email marketing tool you can track the open rate and link click rate to see whose engaging.
Lastly, with conversion points like an inquiry form, downloadable resources, and seminars, you can encourage actions from the customer more easily and use that to guide your approach.
2. Make a data-informed approach
Next step two is to use a marketing automation tool to check their past actions, like when they’ve visited your site, what pages they clicked on, what conversions they had, and so on. Certain pages are more telling of a hot lead than others, for instance, only those that are seriously considering check out the pricing page or the integration flow, and sign up for a seminar, whereas the homepage, benefits, and an educational ebook tend to be on the lower end of the spectrum, as in they aren’t likely to be considering a purchase right now.
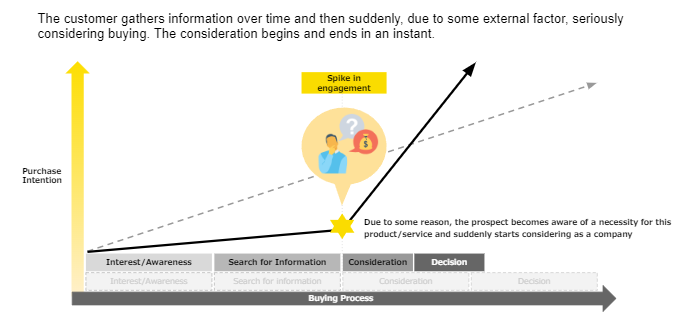
To give some background as to why looking at the customers’ online activity is so important, let’s think about how B2B customers start to consider a purchase.
Many people tend to assume its a more-or-less gradual increase in interest, as the customer gains more and more interest or exposure to your service, but actually, there is always some external factor that causes the customer to suddenly start considering, and this confederation period begins and ends in an instant. The external factor could be that the CEO of a company heard from his friend that they tried Salesforce and were getting amazing results, so the CEO says to his sales manager to go research it for him. Or maybe the contract with their previous service ended and they want to try something new, or perhaps it’s something larger like the pandemic that causes them to try out a new digital tool. But whatever the reason, at this moment, the customer suddenly starts researching intensively online, and it’s key that you catch this timing, so you can reach out and sell to them when they actually have current needs and are open to hear about your service.
3. Integrate inside sales fully into your organization
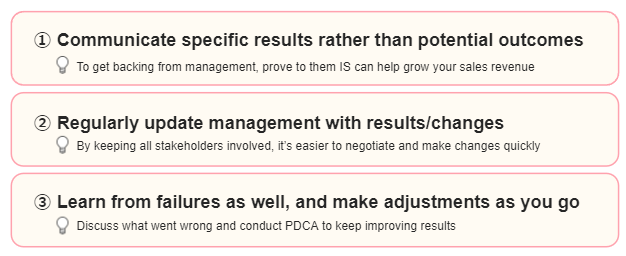
The final step is to make sure inside sales gets fully-established and integrated into your organization. One way to do this is to get management directly involved in the project and report back concrete results to them, so they can feel a sense of progress and get more on board. This will make it easier to make swift changes and improve your sales team and strategy, because there will be less resistance and more support, in terms of both your budget and general backing. Finally, do not get too discouraged if you don't get great results right away. There are bound to be some issues that need solving in the beginning, but just search for the root of the problem and fix as you go along to maximize your results.
Related Articles:
How to Make More Productive Sales Calls with BANT
What is Relationship Marketing? Definition, Benefits, and Strategies




.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)


